Cookbook¶
Producing dust-temperature, dust-mass and 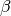 maps from a list of images at
different temperature by fitting multi-greybody components to the spectral
energy distribution at every pixel.
maps from a list of images at
different temperature by fitting multi-greybody components to the spectral
energy distribution at every pixel.
Setup initial guesses¶
The Sed and SedStack classes take initial guesses for temperatures, masses and beta values as input. These variables have to be given as lists with as many entries as there are components to be fitted.
>>> from astrolyze import *
>>> number_of_components = 2
>>> temperature_guesses = [20, 40]
>>> mass_guesses = [1e5, 1e3]
>>> beta_guess = [2]
Note
At the moment only a single beta value for both components can be used.
Prepare the maps with the different wavelength of the SED¶
To create an SedStack you have to have a folder that contains only the maps you want to use. At the beginning these can still have different formats, resolution and other parameters. You can use the Stack class to unify the maps. Especially to construct temperature and mass maps from these maps, the Stack of maps has to have the same resolution, flux unit, and dimensions (map/pixel size). In the following the process of unifying a set of images is shown.
>>> stack_ = Stack("InputFolder")
>>> stack_ = stack_.unify_units(unit="JyB", folder="output_folder1")
>>> stack_ = stack_.unify_resolutions(folder="output_folder2") # Default uses larges resolution found
>>> stack_ = stack_.unify_dimensions(template="template_map", folder="output_folder3")
Here template_map is a map that has the dimension and pixel size one ones to obtain for the final SED-maps. output_folder1-3 should be physically distinct.
Loadind the SedStack and fitting¶
Now one can load the final stack of images and produce the SED maps
>>> sed_stack = SedStack('output_folder3', full_map=true, flux_acquisition='pixel', number_components=2, temperature_guesses=temperature_guesses, mass_guesses=mass_guesses, beta_guess=beta_guess)
>>> sed_stack.get_sed_maps(folder="final_output_folder")